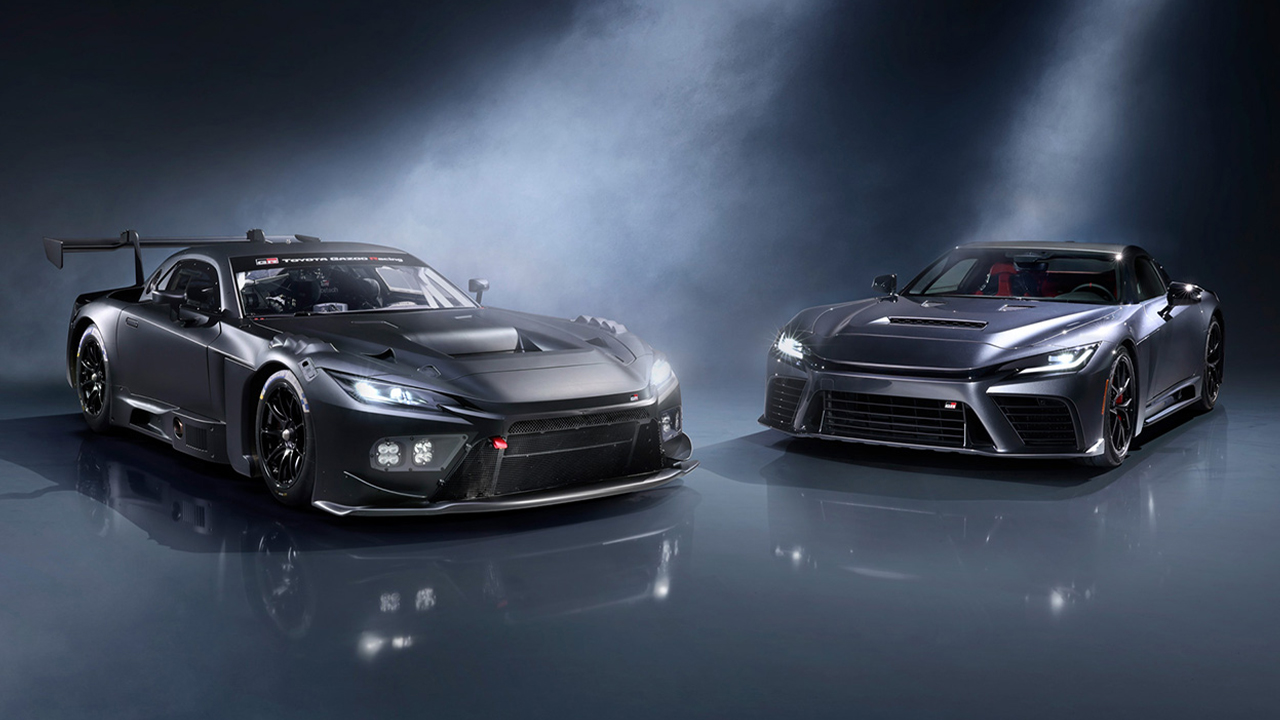
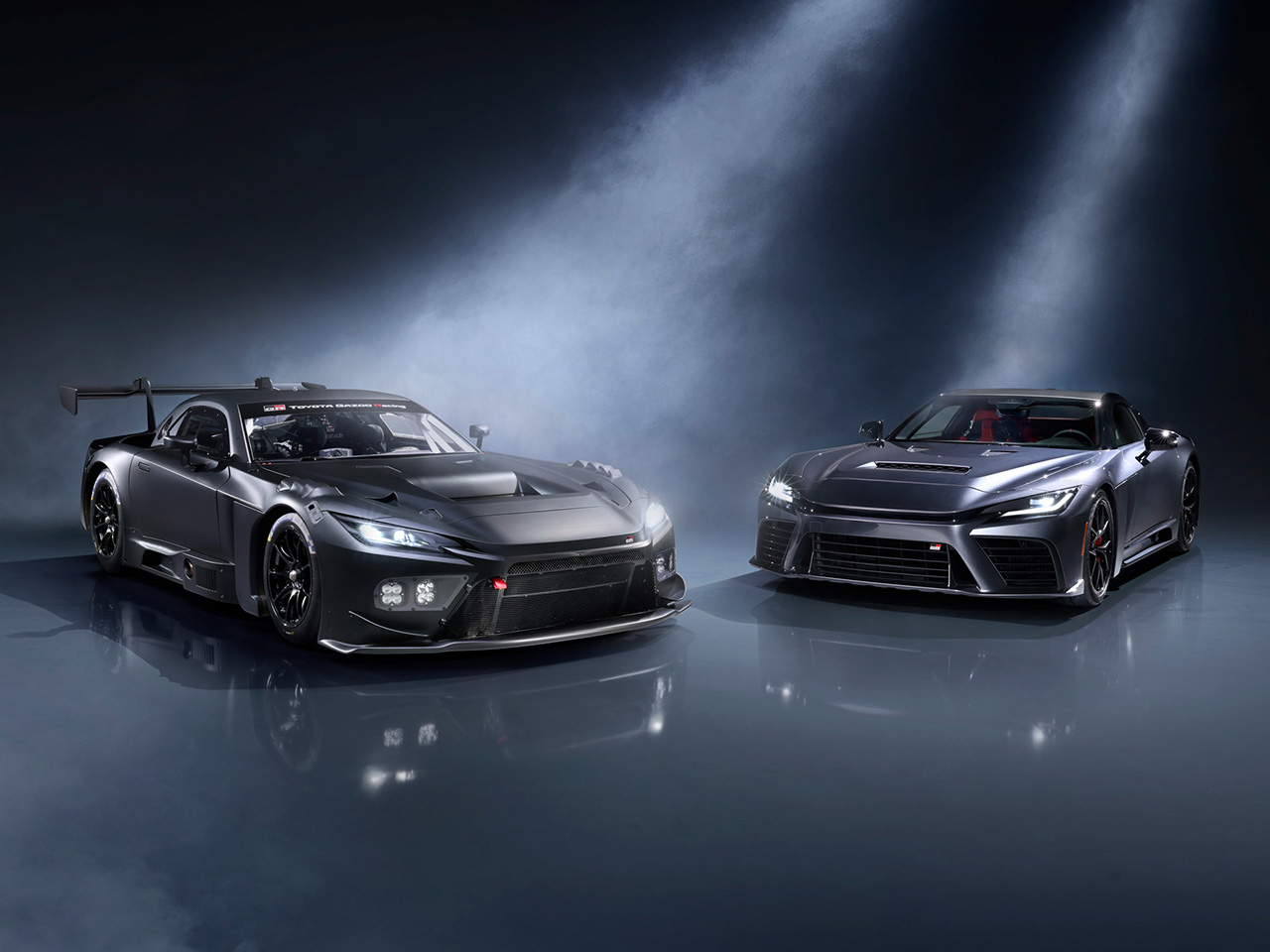
TOYOTA GAZOO Racing (TGR) has unveiled two new models—the GR GT and GR GT3—showcasing their development prototypes to the public for the first time. Both models enhance three key performance pillars: a low center of gravity, lightweight construction with high rigidity, and superior aerodynamics.
The GR GT is TGR’s new flagship sports car, developed with the concept of a race car engineered for everyday road use. The GR GT3, on the other hand, is a full FIA GT3–spec race car developed from the GR GT, created for customers aiming to win races. Both vehicles adopt new technologies and manufacturing processes, including Toyota’s first-ever full aluminum body structure and a newly developed 4.0-liter twin-turbo V8 engine.
The GR GT and GR GT3 are positioned as Toyota’s next-generation flagships, following the legacy of the Toyota 2000GT and Lexus LFA. Their development embodies the concept of passing down the “secret formula of car-building” from one generation to the next—a philosophy Toyota calls “Shikinen Sengu.” This approach blends the expertise of the LFA development team with Toyota’s latest technologies being applied for the first time.
The GR GT is engineered as a race car that is fully road-legal. It uses a hybrid system combining a newly developed 4.0-liter twin-turbo V8 with an electric motor, targeting a system output of over 650 PS and torque of over 850 Nm. Development focuses on lowering the center of gravity, reducing weight, strengthening the body, and maximizing aerodynamic efficiency.
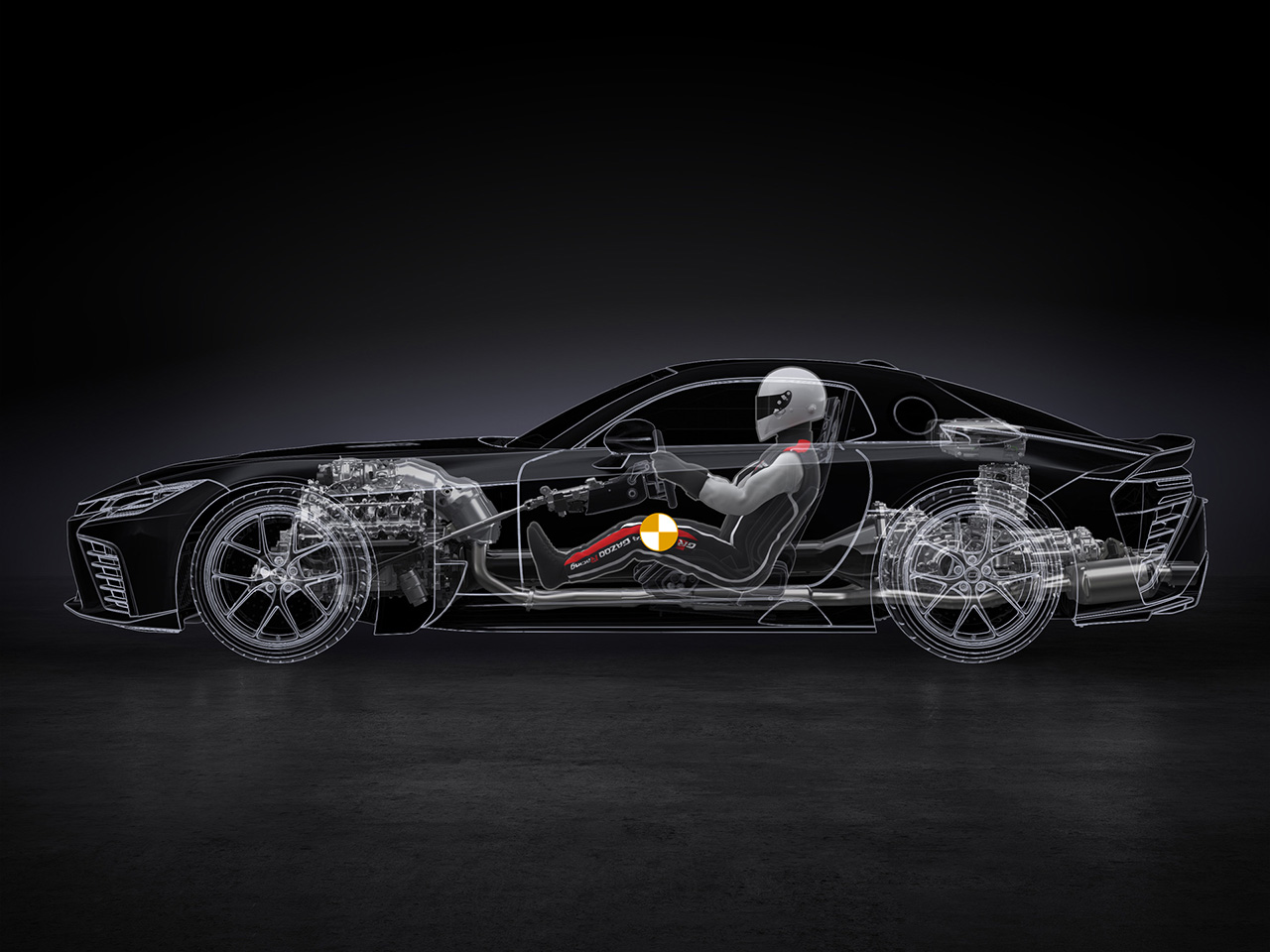
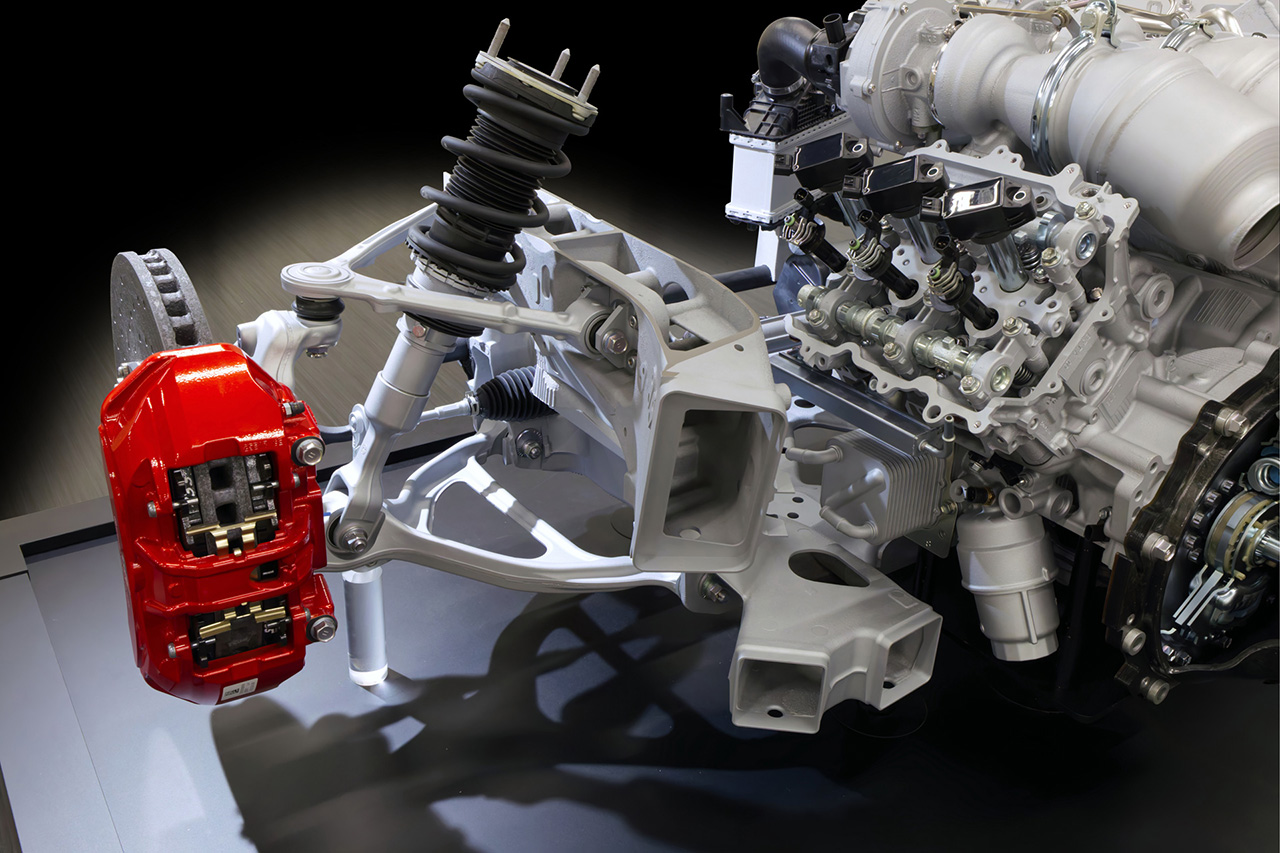
The vehicle is designed with the lowest possible center of gravity by lowering the overall height and driver position, while adopting a front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout for controllability near the limit. Heavy components—such as the V8 engine with a dry-sump system, rear transaxle, and other key elements—are positioned as low as possible, placing the driver’s center of gravity close to that of the car for a stronger sense of unity.
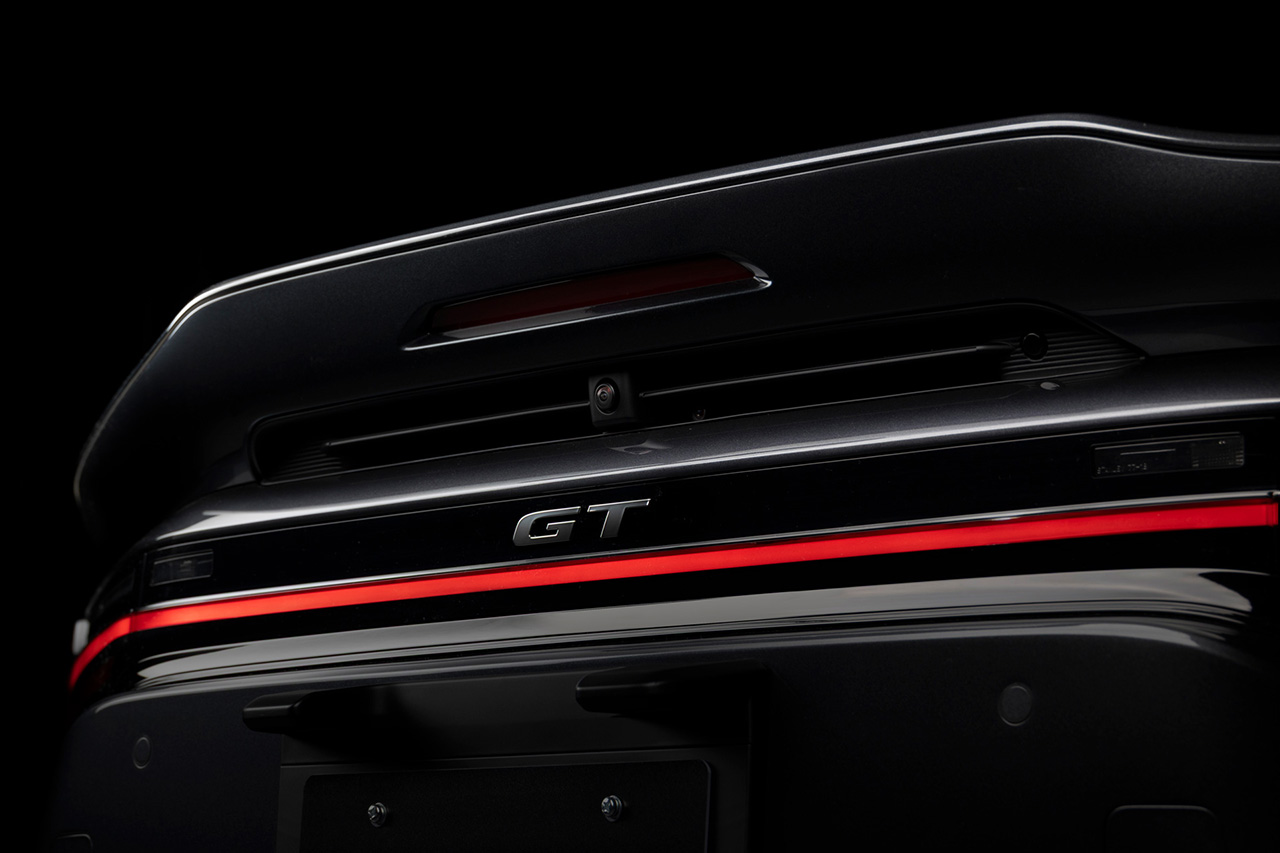
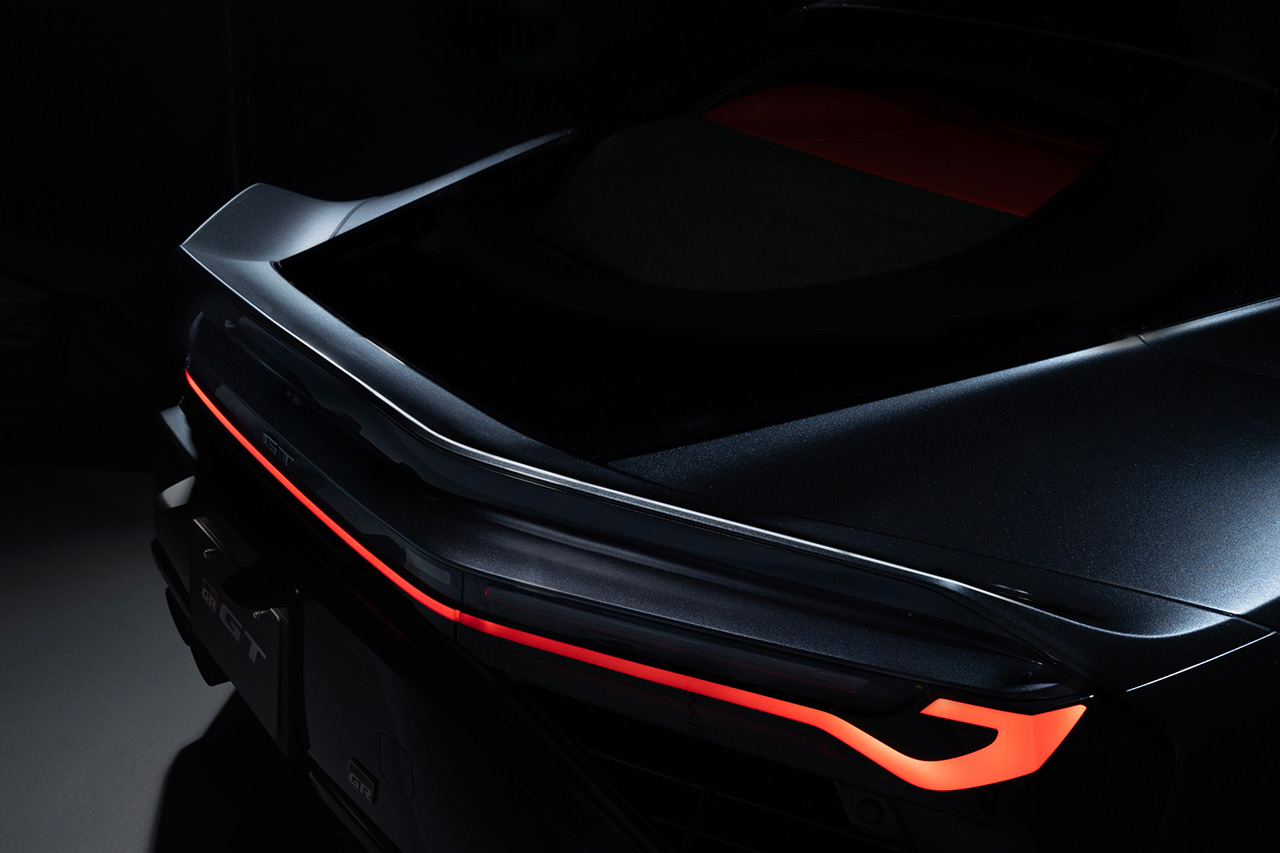
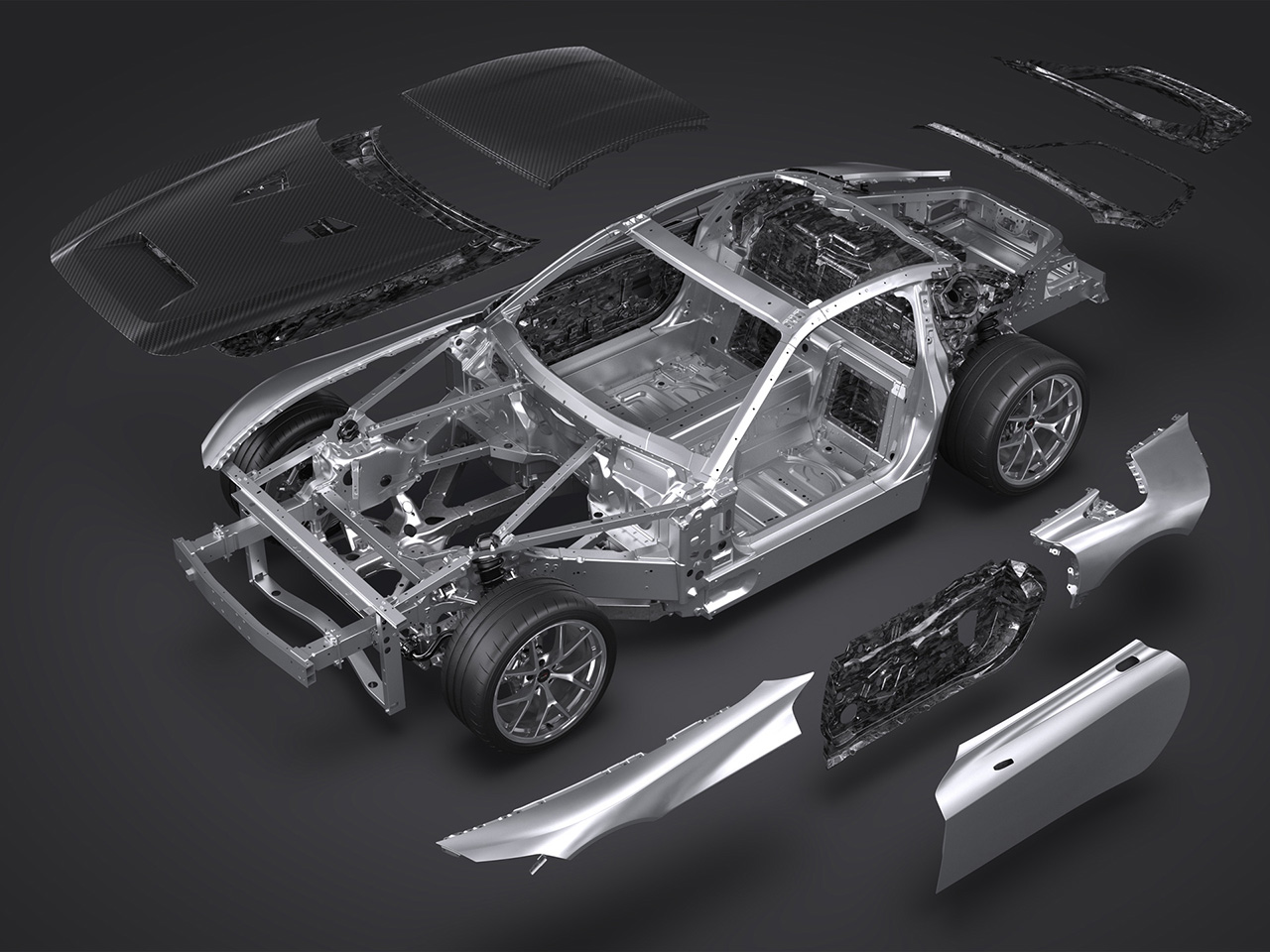
The GR GT uses Toyota’s first fully aluminum body structure, combined with CFRP, plastics, and other lightweight materials, resulting in a strong yet lightweight chassis. The exterior design prioritizes aerodynamic performance.
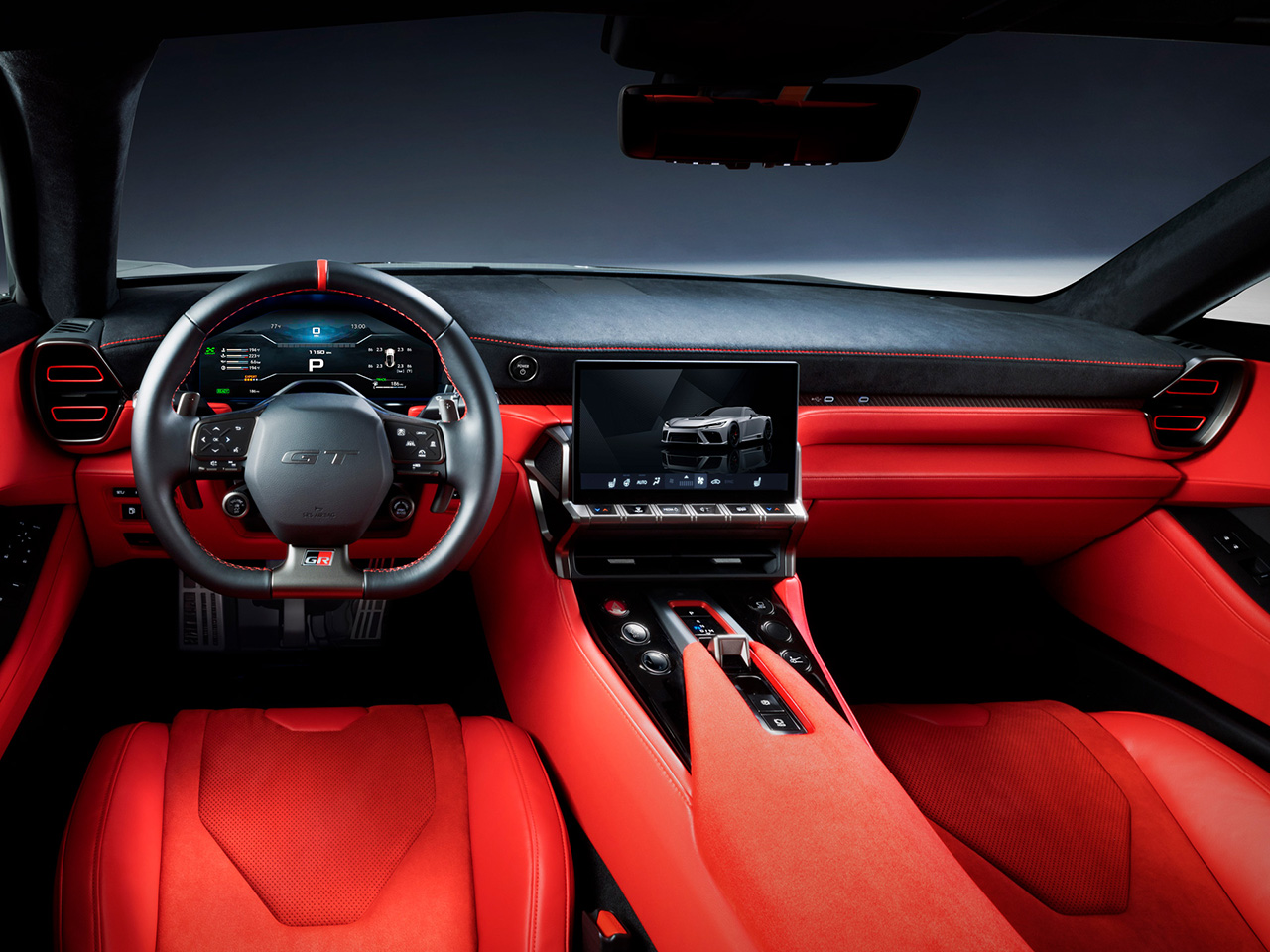
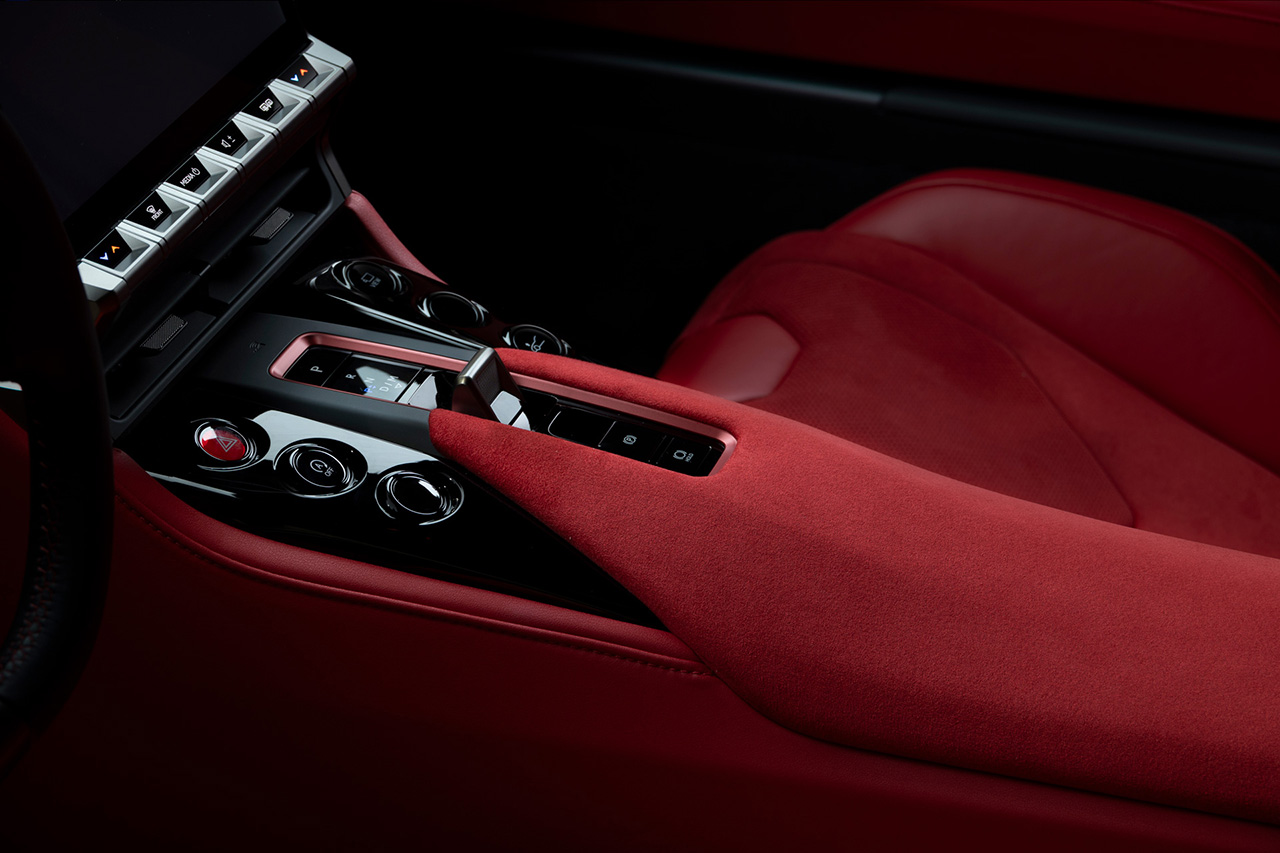
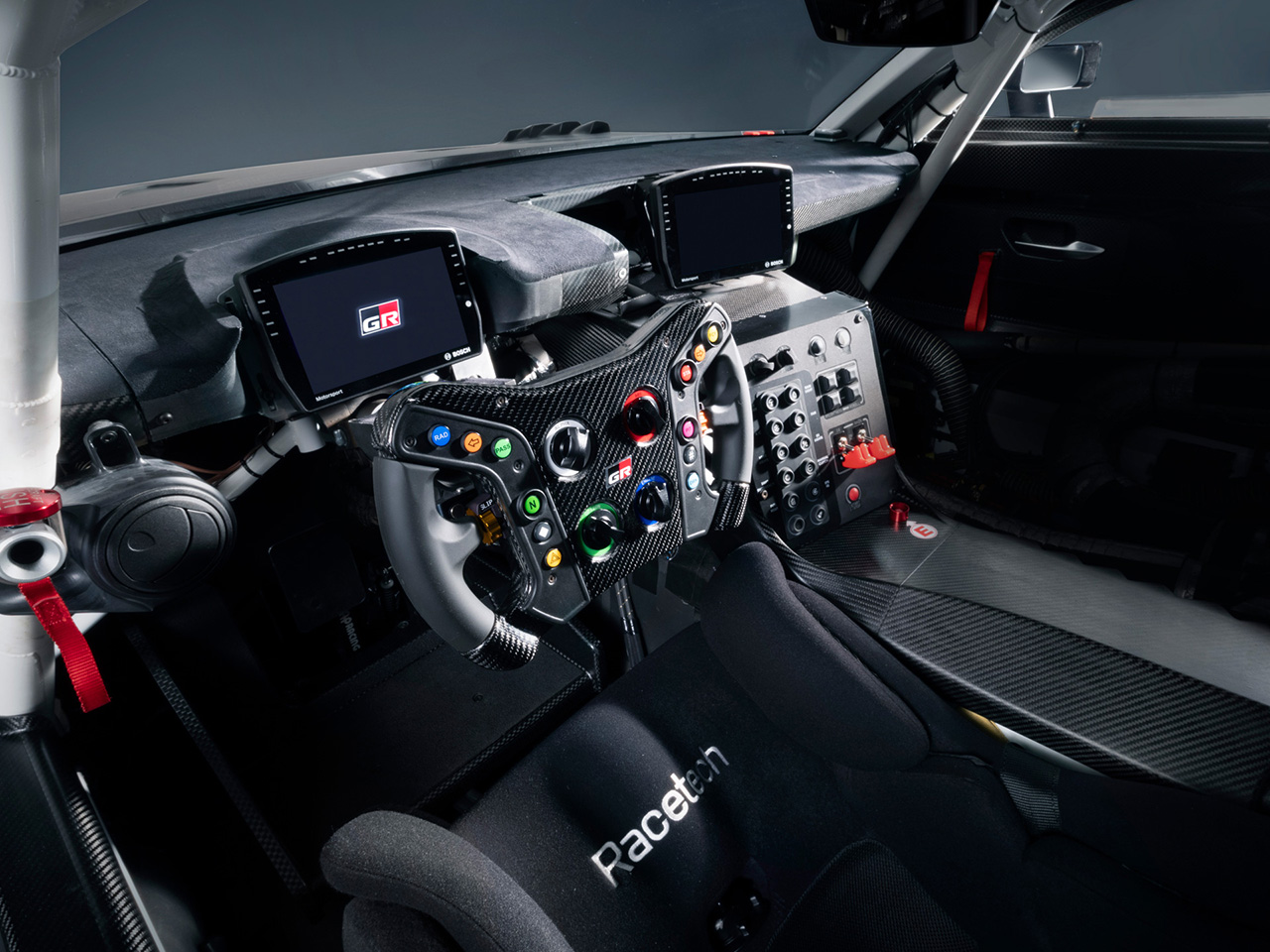
Inside, the cabin is designed to provide optimal driving position and visibility for both racers and everyday drivers. Controls are placed within easy reach, and the TFT LCD instrument cluster is engineered for clear visibility even at high speeds or during track driving.
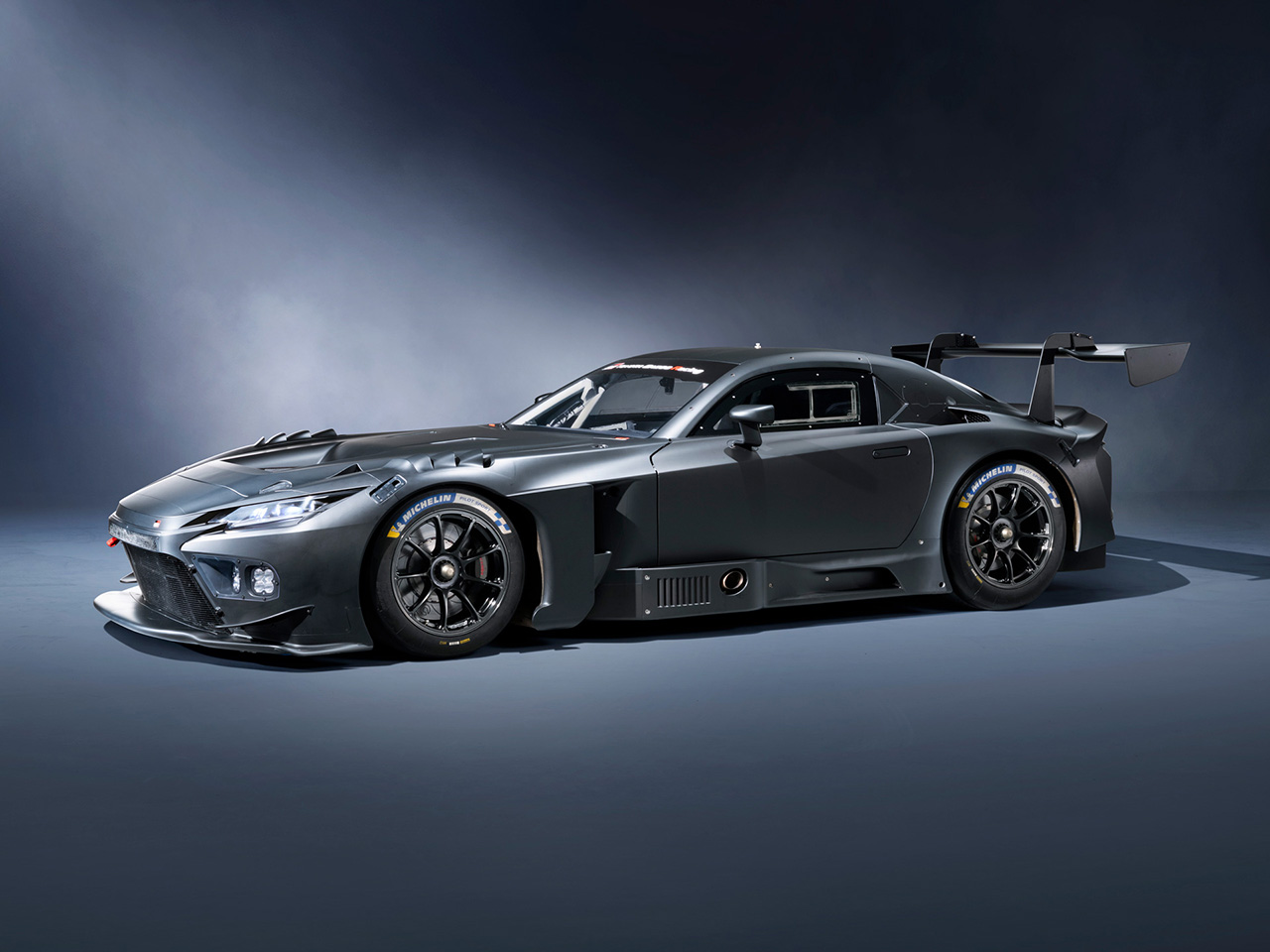
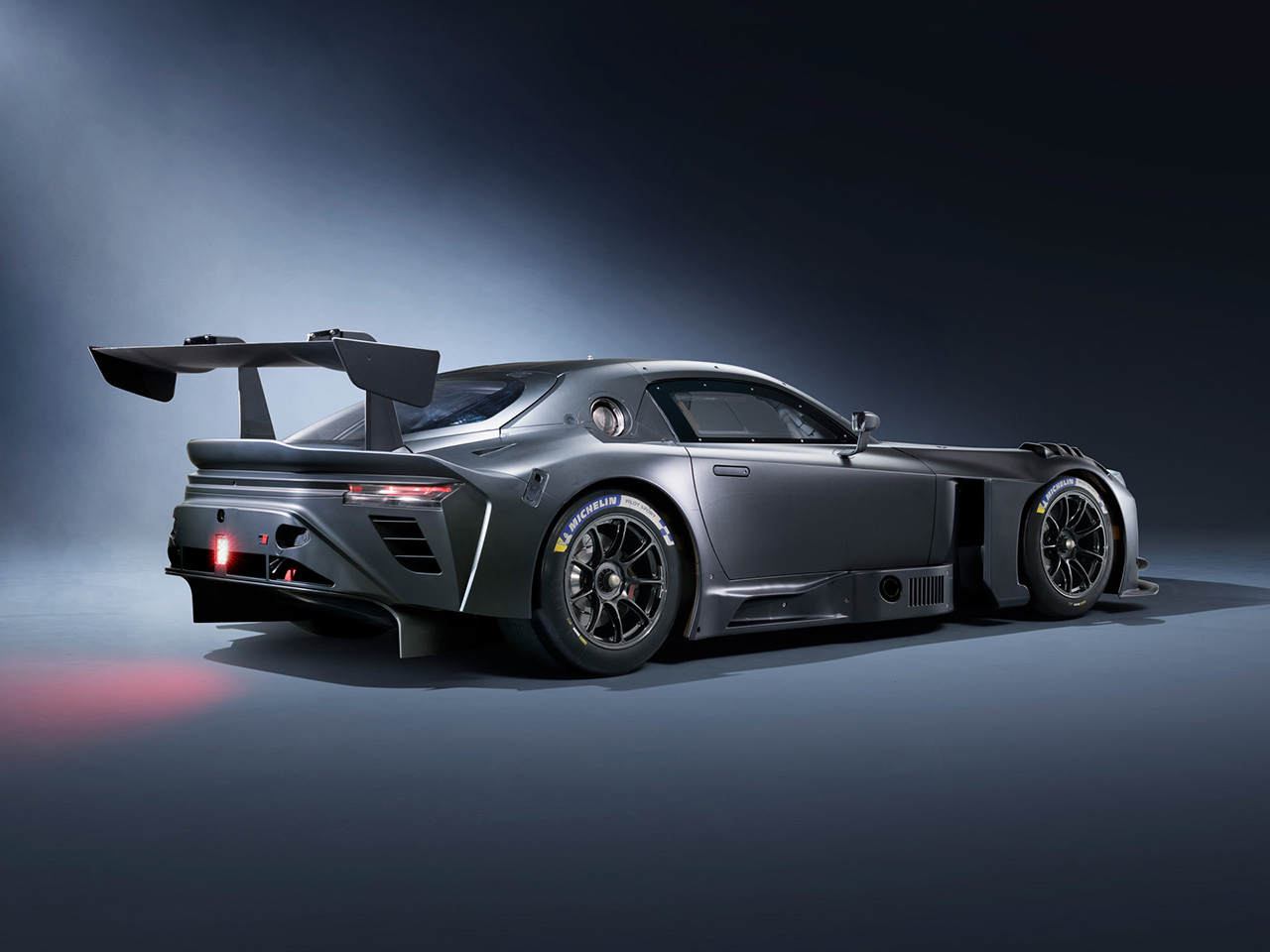
The GR GT3 is built on the same foundation as the GR GT, retaining the core attributes of a low center of gravity, lightweight construction, and excellent aerodynamics. The model is fully compliant with FIA GT3 regulations.
Development of both the GR GT and GR GT3 includes not only new technologies but also new development processes, such as using a racing-grade simulator from the early stages to accelerate chassis tuning. Physical testing is also conducted at Shimoyama, Fuji Speedway, Nürburgring, and even on public roads. TGR continues to advance development, targeting a market launch around 2027.
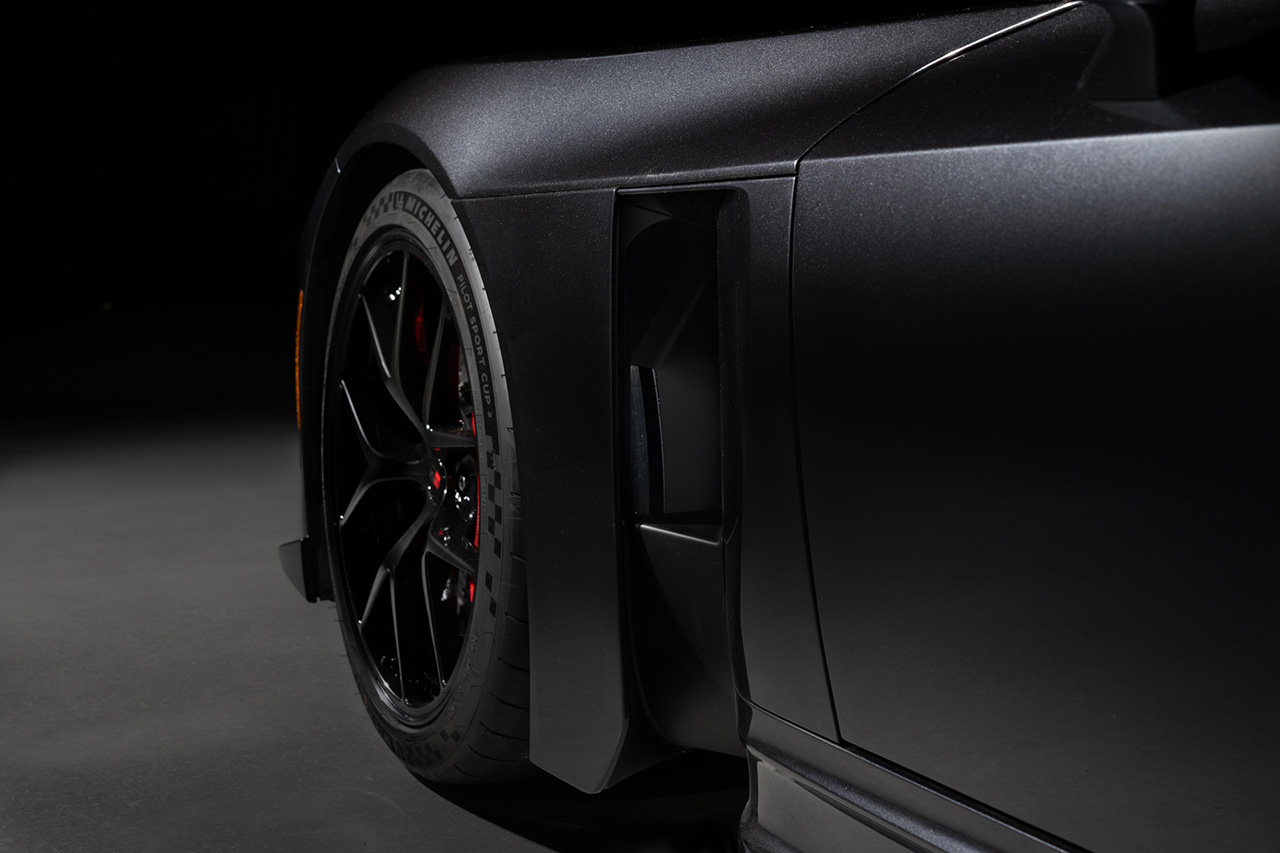
The GR GT’s design focuses heavily on aerodynamics and cooling performance, with engineers from Toyota’s WEC racing program participating in development. With a top speed exceeding 320 km/h, efficient airflow and downforce are essential. The design process began with aerodynamic modeling before moving to production-style exterior design.
The interior emphasizes usability and control, with optimized space and visibility for both road and track use. Key controls are positioned around the steering wheel to minimize the need for eye movement. The instrument cluster underwent repeated refinement to achieve ideal size, position, and visibility in any scenario.
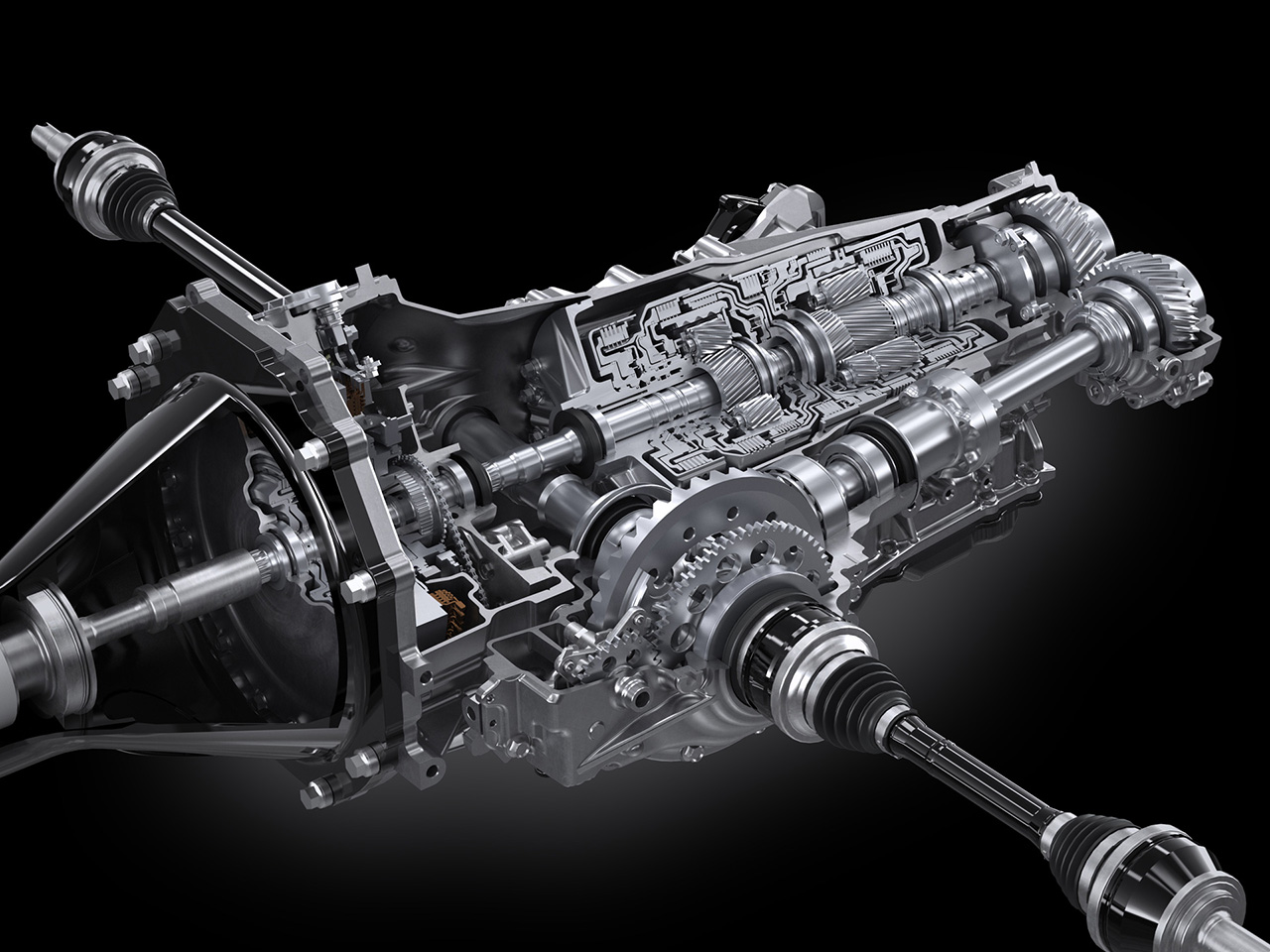
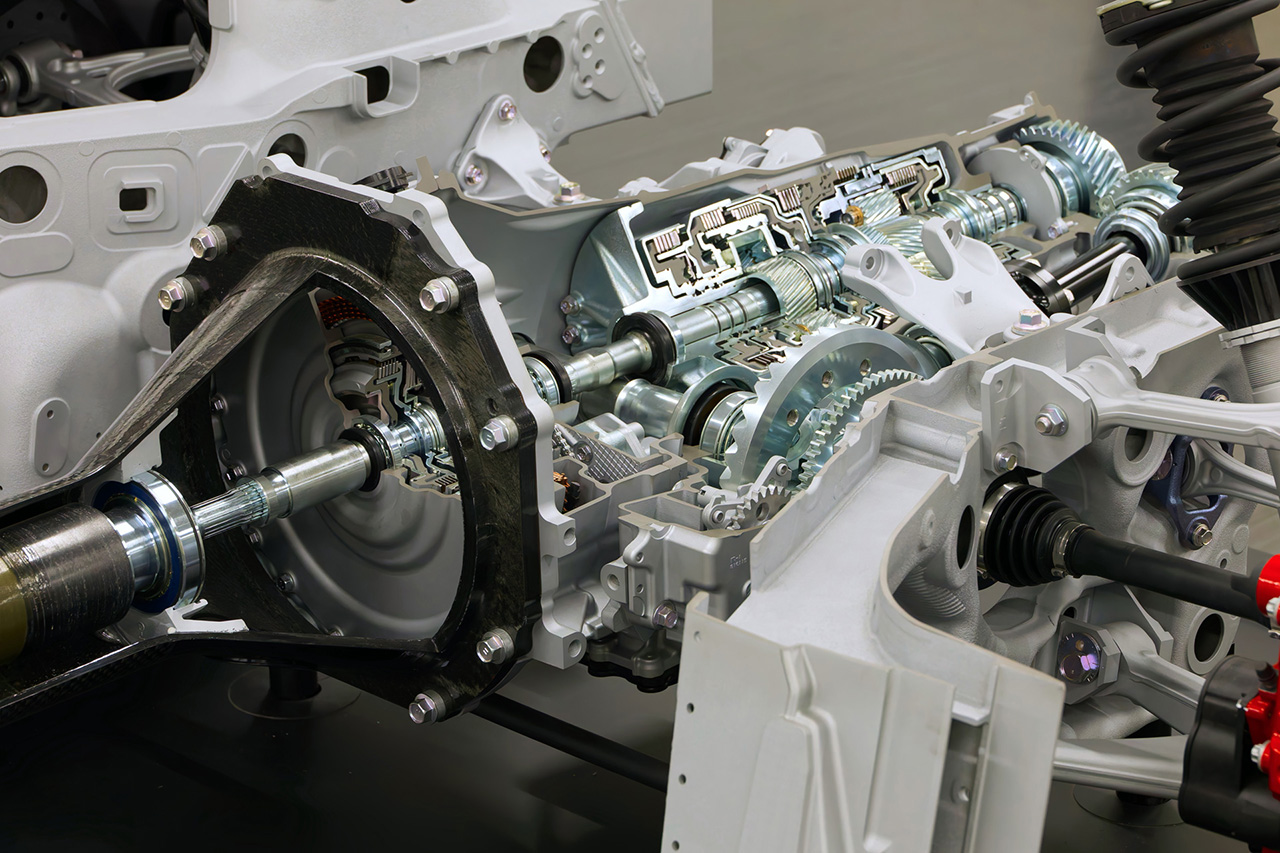
The 4.0-liter twin-turbo V8 used in the GR GT is Toyota’s first twin-turbo V8 designed for a production vehicle. Compact and lightweight, it was engineered to support the GR GT’s low-center-of-gravity concept. It features a hot-V layout, dry-sump lubrication, a CFRP torque tube connecting to a rear transaxle, a new 8-speed wet-clutch automatic transmission, and a mechanical limited-slip differential. This results in a front–rear weight distribution of 45:55.
The GR GT also emphasizes engine sound, with an exhaust system designed to deliver motorsport-inspired acoustics and respond naturally to throttle inputs—whether idling, accelerating, or decelerating.
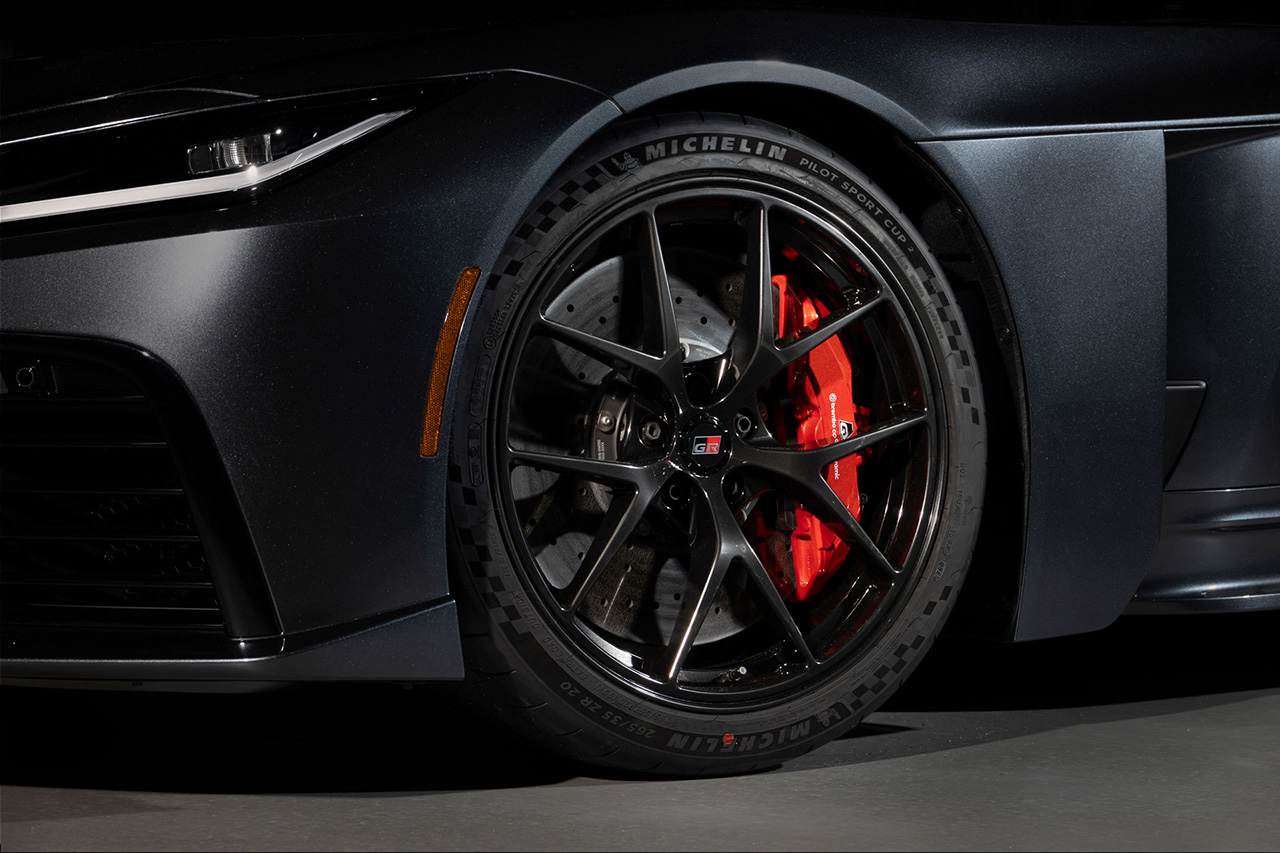
The aluminum body structure provides high rigidity with reduced weight. The all-new double-wishbone suspension (front and rear) is paired with Michelin Pilot Sport Cup 2 tires developed specifically for the model. Braking is handled by Brembo carbon brakes, with adjustable stability control. The aluminum chassis and suspension architecture are engineered to be shared with the GR GT3.
GR GT Specifications
The body structure features a full aluminum frame with seating for two. Vehicle weight is capped at 1,750 kg, with a front–rear weight distribution of 45:55.
The powertrain consists of a 3,998 cc engine with an 87.5 x 83.1 mm bore and stroke, a twin-turbo V8 paired with a hybrid motor integrated into the transaxle. Power is sent through a newly developed 8-speed automatic transmission. System output is over 650 PS and system torque exceeds 850 Nm.
The layout is front-engine, rear-wheel drive. Both front and rear suspension use double-wishbone setups with coil springs. Braking is provided by carbon-ceramic discs front and rear. Tire sizes are 265/35ZR20 in front and 325/30ZR20 at the rear. Top speed exceeds 320 km/h.
GR GT Dimensions
-
Length: 4,820 mm
-
Width: 2,000 mm
-
Height: 1,195 mm
-
Wheelbase: 2,725 mm
GR GT3 Specifications
The GR GT3 uses a 3,998 cc V8 twin-turbo engine without an electric motor, with a front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout.
GR GT3 Dimensions
-
Length: 4,785 mm
-
Width: 2,050 mm
-
Height: 1,090 mm
-
Wheelbase: 2,725 mm



















.jpg)




Source: Toyota Global Newsroom